USB, the standard is called Universal Serial Bus, which is a communication protocol for data exchange between computers and peripheral devices.
Like USB2.0 or USB3.1, it refers to the transmission standard;
And USB Type-C or USB Type-A, it refers to the physical interface type.
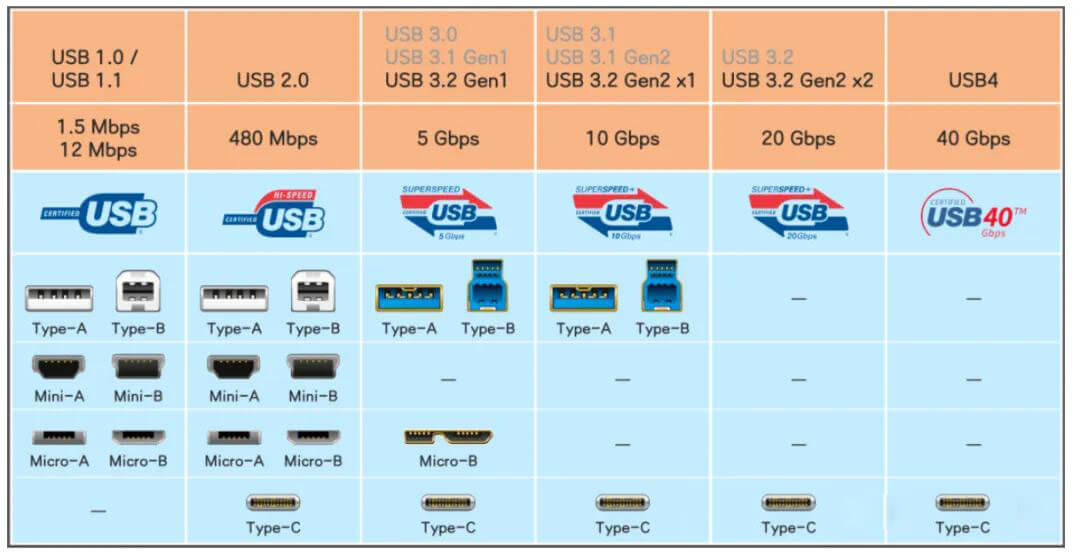
1. USB Interface Types
Let’s first take a look at the current USB transmission standards and corresponding interface types:
1.1 Standard USB interface, divided into Type-A and Type-B
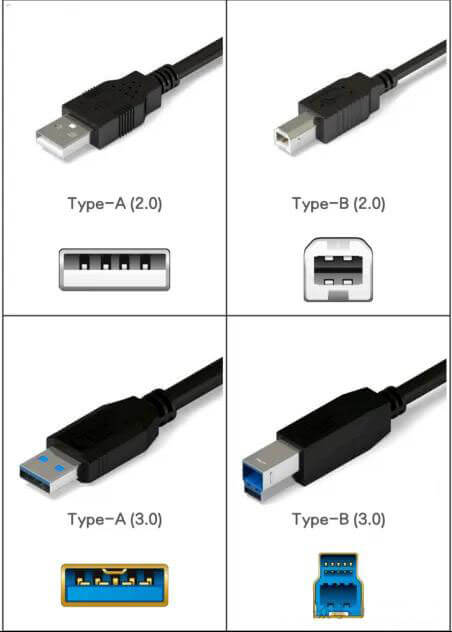

According to the color of the interface, we can easily distinguish whether the interface supports USB2.0 or USB 3.0.
Type-A interface is also the most common USB interface in our daily life, widely used in devices such as mouse, keyboard, USB flash drive, etc. Type-B is often used in printers and special monitors.
1.2 Mini USB interfaces are mainly divided into Mini-A and Mini-B
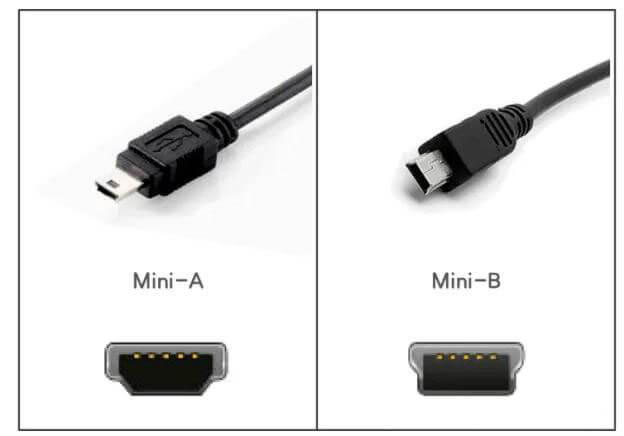

Mini USB interface is a small USB interface with the same specifications as standard USB,
but with an ID pin (used to distinguish whether the device is a host or a peripheral) added to support OTG function.
1.3 Micro USB interface
Micro USB is the next generation interface of Mini USB.
The plug of Micro USB interface is made of stainless steel, and the plug-in life is increased to 10,000 times.
Compared with Mini USB interface, the height is halved while the width remains unchanged, making it more compact.
Micro USB interface can also be divided into Micro-A and Micro-B
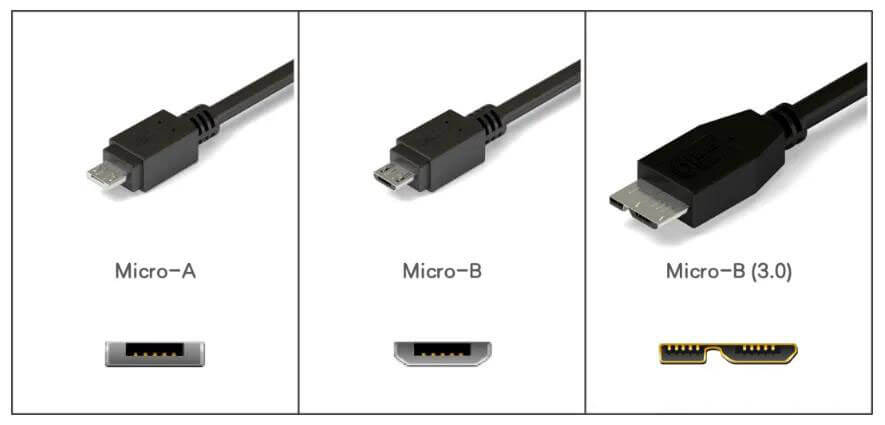

I believe everyone knows the Micro-B type USB interface, but they just don’t know its professional name.
In the early days of smartphone development, most smartphones (except Apple phones) used Micro-B as a charging and data interface.
After the release of the USB 3.0 standard, the Micro-B interface also has a new shape, and I believe everyone is familiar with it.
Most of the mobile hard disk boxes that support USB 3.0 that we buy use the Micro-B interface.
1.4 Type-C interface
For users, the biggest advantage of the Type C interface is that it can be plugged in and out in both directions.
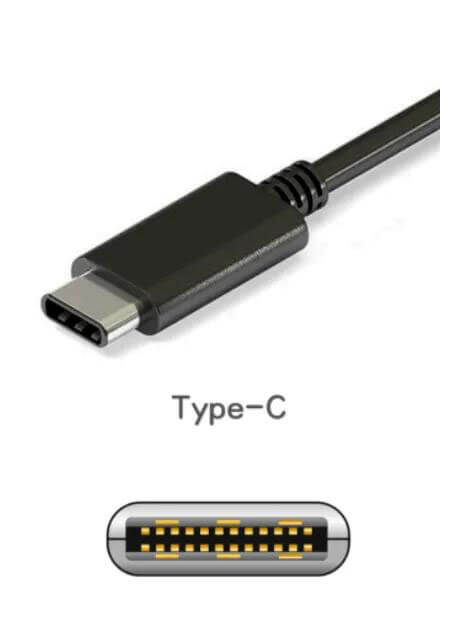

The latest USB4 standard currently only supports Type-C interface.
At the same time, USB4 adopts Thunderbolt protocol (commonly known as Thunderbolt interface protocol, which is an interface protocol developed by Intel, with fast speed and compatibility with multiple interfaces/protocols such as Thunderbolt, USB, Display Port, PCIe, etc. when powering).
Therefore, the Type-C interface that supports USB4 standard is also compatible with Thunderbolt interface.
2. Pin Definitions
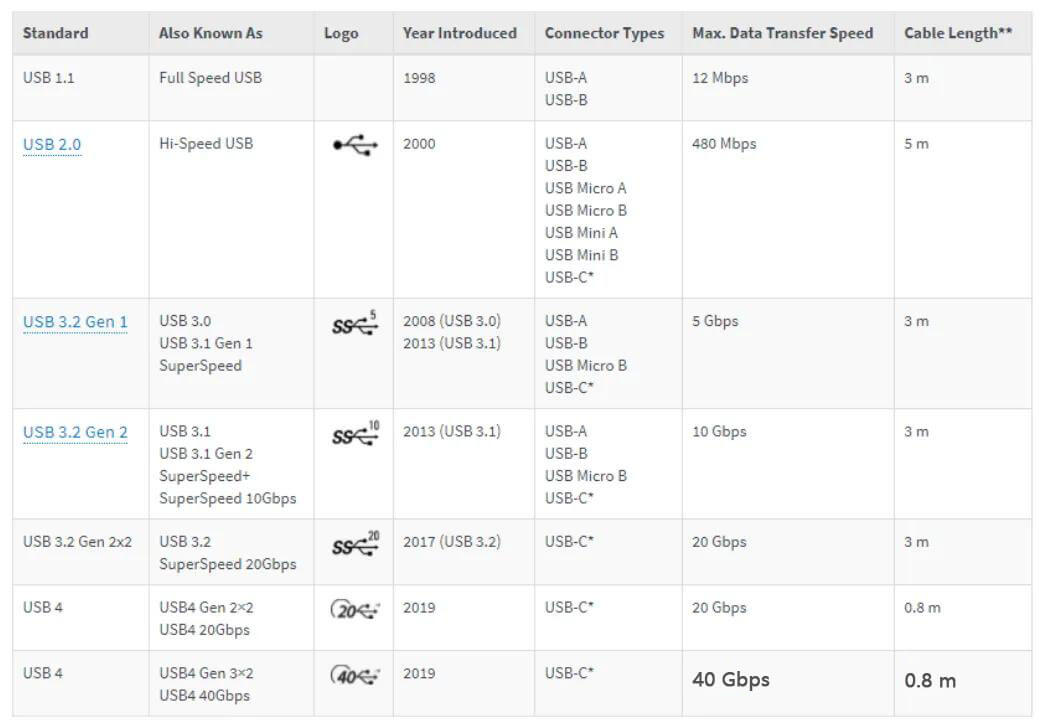
After knowing the appearance of various interfaces, let’s take a look at their respective pin definitions.
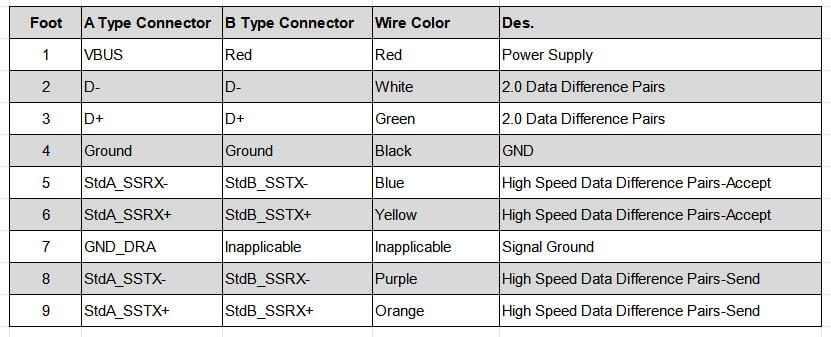
2.1 USB1.1/2.0 Type-A/TYPE-B interface pin definition and color
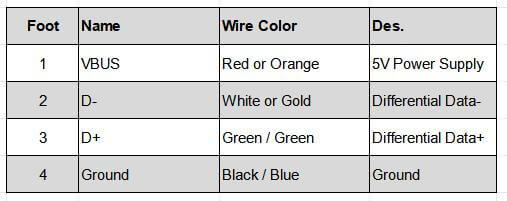
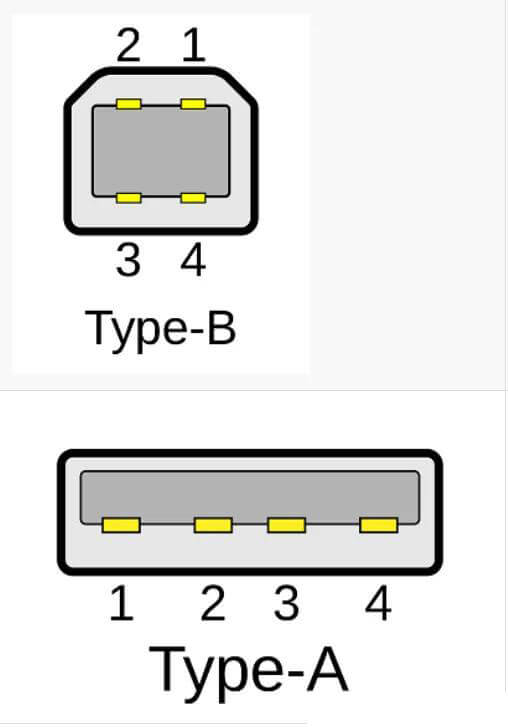
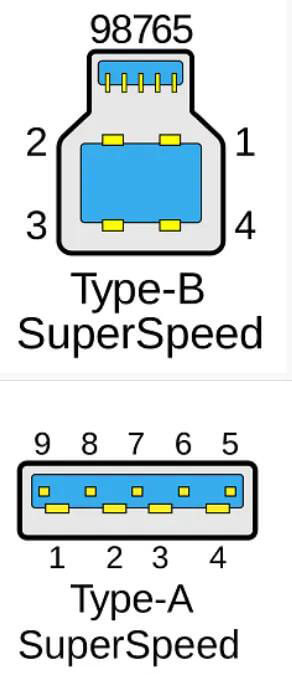
2.2 Pin definition and color of USB3.0 interface and above
2.3 Type-C interface wiring definition
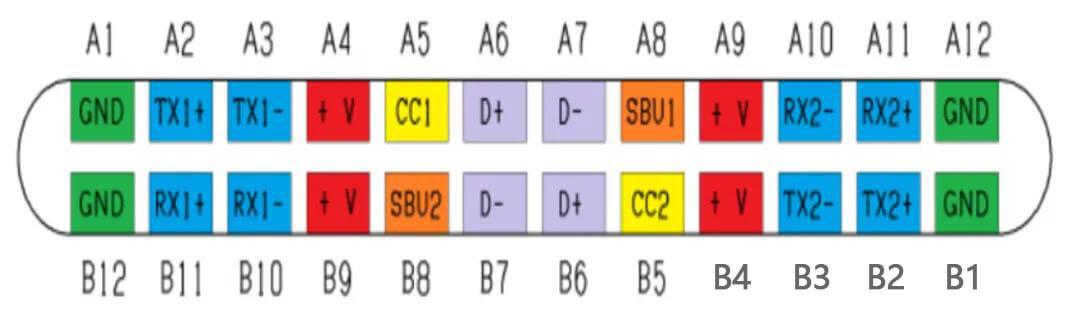
The 24-pin USB Type-C connector can be divided into seven functional types:
- VBUS: Four power pins that allow voltages up to 20 V (A4, A9, B4, B9)
- CCx: Two configuration channels for protocol communication (A5, B5)
- VCONN: Provides cable configuration IC (on the socket, it is one of the CC pins)
- SuperSpeed Lane1: Has RX differential pair RX1p, RX1n and TX differential pair TX1p, TX1n
- SuperSpeed Lane2: Has RX differential pair RX2p, RX2n and TX differential pair TX2p, TX2n
- SBU1,2: Sideband lines for alternate mode
- D+, D-: USB 2.0 high-speed signals
- GND: Four ground pins
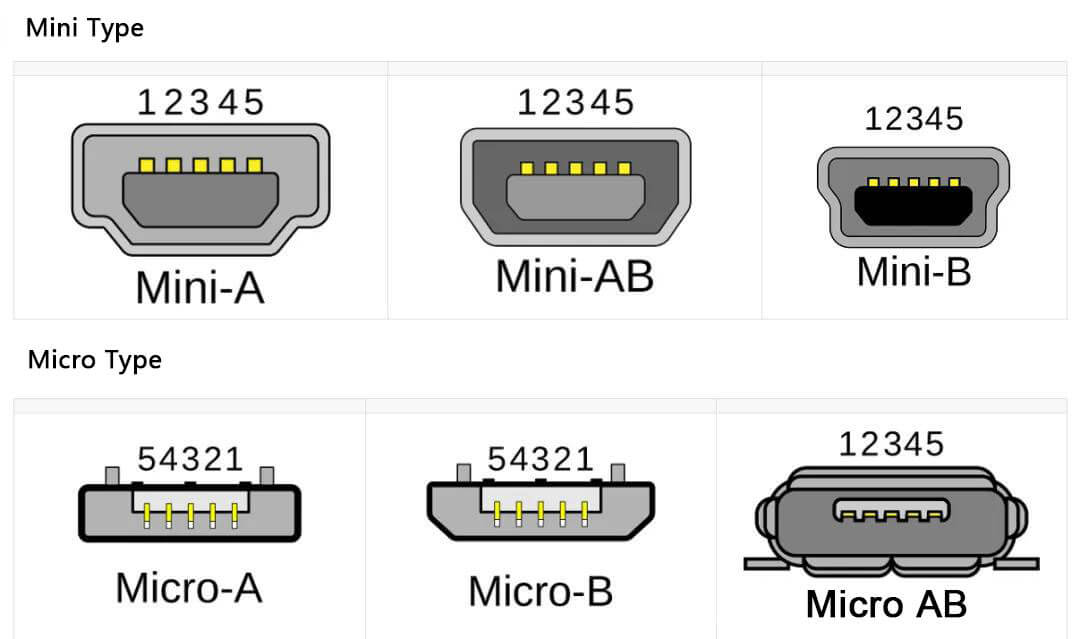
2.4 Mini/Micro-A/B pin definition and color
Mini USB has the same interface functions as standard USB except for pin 4.
Pin 4 becomes ID, and the ground wire is connected to pin 5 on mini-A, and can be left floating or connected to pin 5 on mini-B.

Finally, let’s summarize: